Digitalization as an Enabler for Women’s Empowerment
Topic
Gender inequalities persist worldwide, favouring one gender over the other and hindering social justice and sustainable development. Recognizing this problem, the United Nations has integrated gender equality into the Sustainable Development Goals. Digitalization has the potential to empower women by providing access to education, healthcare, employment, and entrepreneurship. However, implementing effective interventions is challenging due to cultural and societal contexts, and Western perspectives may not be universally applicable.
Relevance
The topic of this master's thesis is highly relevant as it examines the impact of digitalization on gender inequality in both developed and developing countries. Understanding the relationship between digitalization and women's empowerment is critical for policymakers, organizations, and stakeholders seeking to promote gender equality. By identifying the specific factors that contribute to reducing gender inequality, practitioners can develop effective strategies and interventions to harness the power of digitalization for women's empowerment.
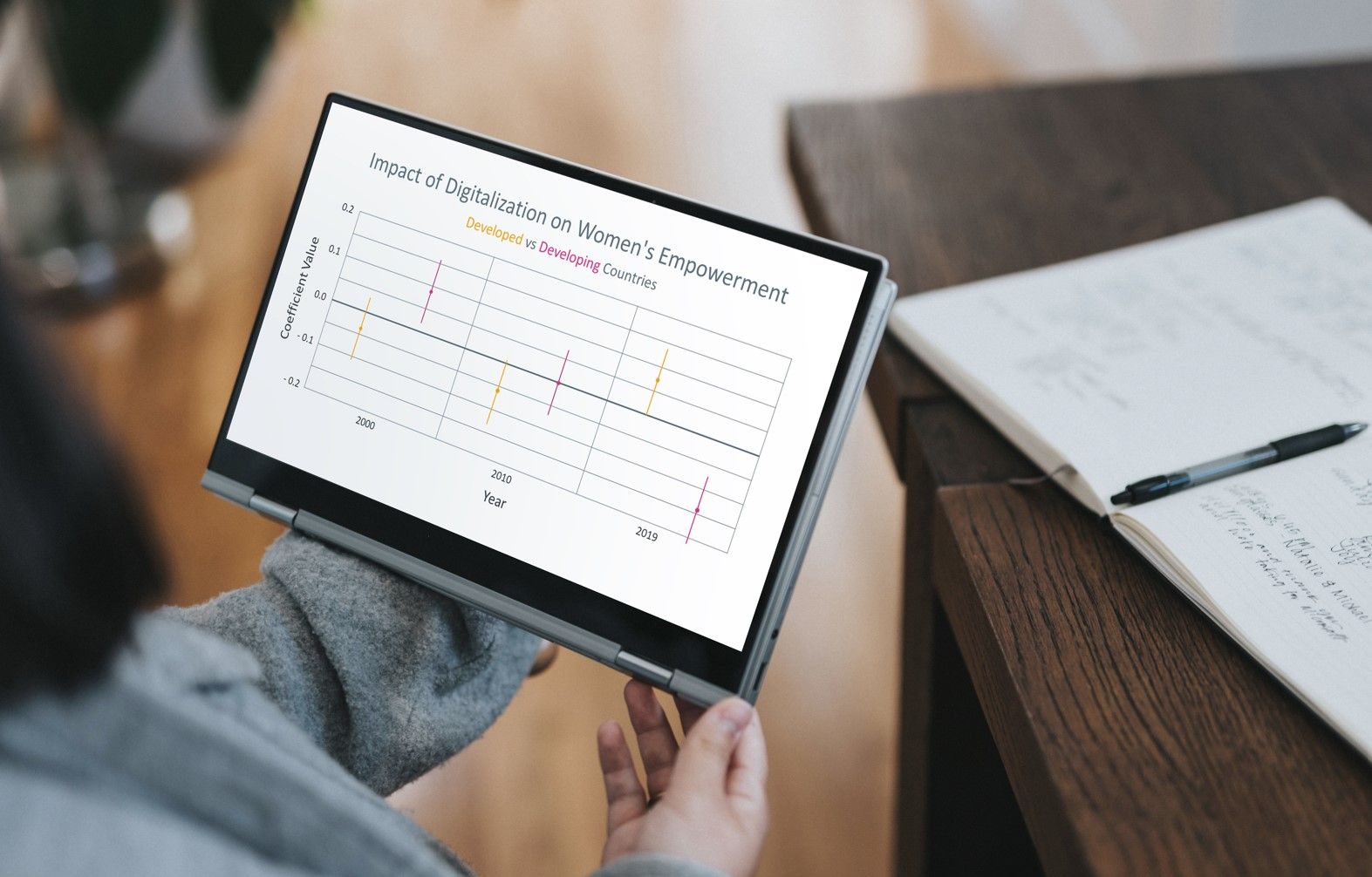
Results
The results of the master's thesis suggest that reductions in gender inequality are associated with improvements in various aspects of development in both developed and developing countries. The study found negative correlations between the Gender Inequality Index (GII) and most indicators, underscoring the multifaceted nature of gender inequality. The study also revealed the importance of digital connectivity, with internet use in particular showing a significant negative correlation with the GII.
Implications for Practitioners
- Recognize the importance of taking into account the level of development when implementing digitalization initiatives to promote women's empowerment and gender equality.
- Tailor strategies and actions to the specific socio-economic context of each country in order to maximize the impact of digitalization on women's empowerment.
- Address barriers to women's access to and use of digital technologies, particularly in developing countries.
- Foster collaboration and knowledge sharing among practitioners, policy makers and stakeholders to harness the potential of digitalization for women's empowerment.
Methods
The master's thesis took a quantitative research approach, using secondary data from public sources such as the United Nations Development Program, the World Bank, and Our World in Data. The study used linear regression analysis and the difference-in-differences (DiD) method on 160 countries and a time period from 2000 to 2019. Digitalization indicators, including individuals using the Internet, mobile phone subscriptions, and fixed broadband subscriptions, were included in the analysis to examine their impact on gender inequality.
