Value of Robots in practical care work
Topic
This Master Thesis explores whether robots can bring value to care workers and what conditions need to be met for these benefits to be realized. By studying how robots can assist in providing care and considering the factors contributing to their success, this research aims to understand how robots can improve the quality of care and bring value to care workers.
Relevance
The relevance for care workers is significant due to the increasing demand for their services caused by demographic aging. The aging population in Switzerland results in a higher number of elderly people requiring care. The shortage of care workers is projected to worsen in the coming years, with a predicted need for an additional 36,500 people by 2029. The research paper explores the potential value of robots to the care sector, addressing the need for innovative solutions to support and enhance care work. By analyzing three use cases of robots in care work, Lio, Paro, and the exoskeleton, the study aims to provide recommendations for maximizing the value and addressing challenges and risks associated with their implementation.
Results
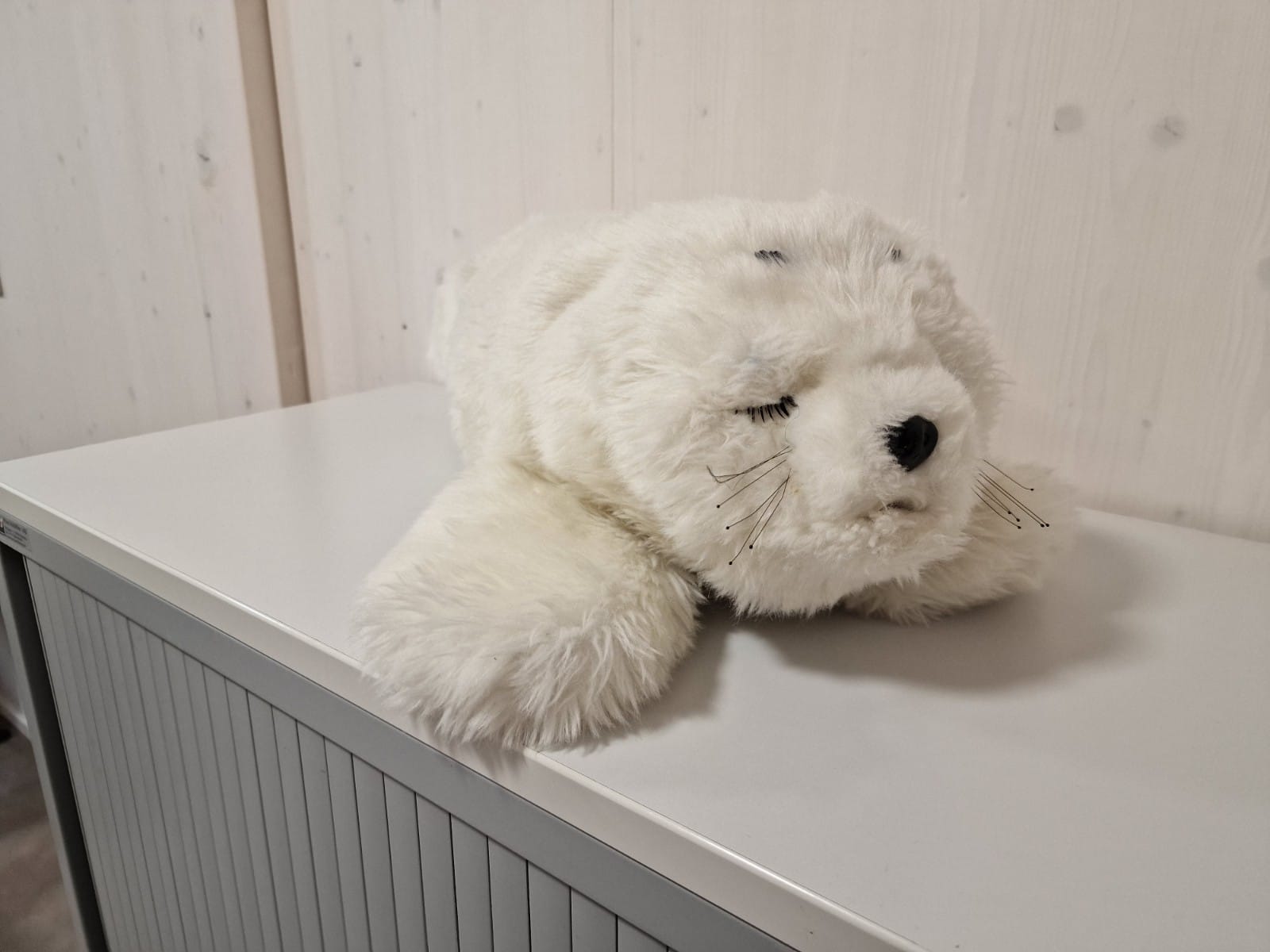
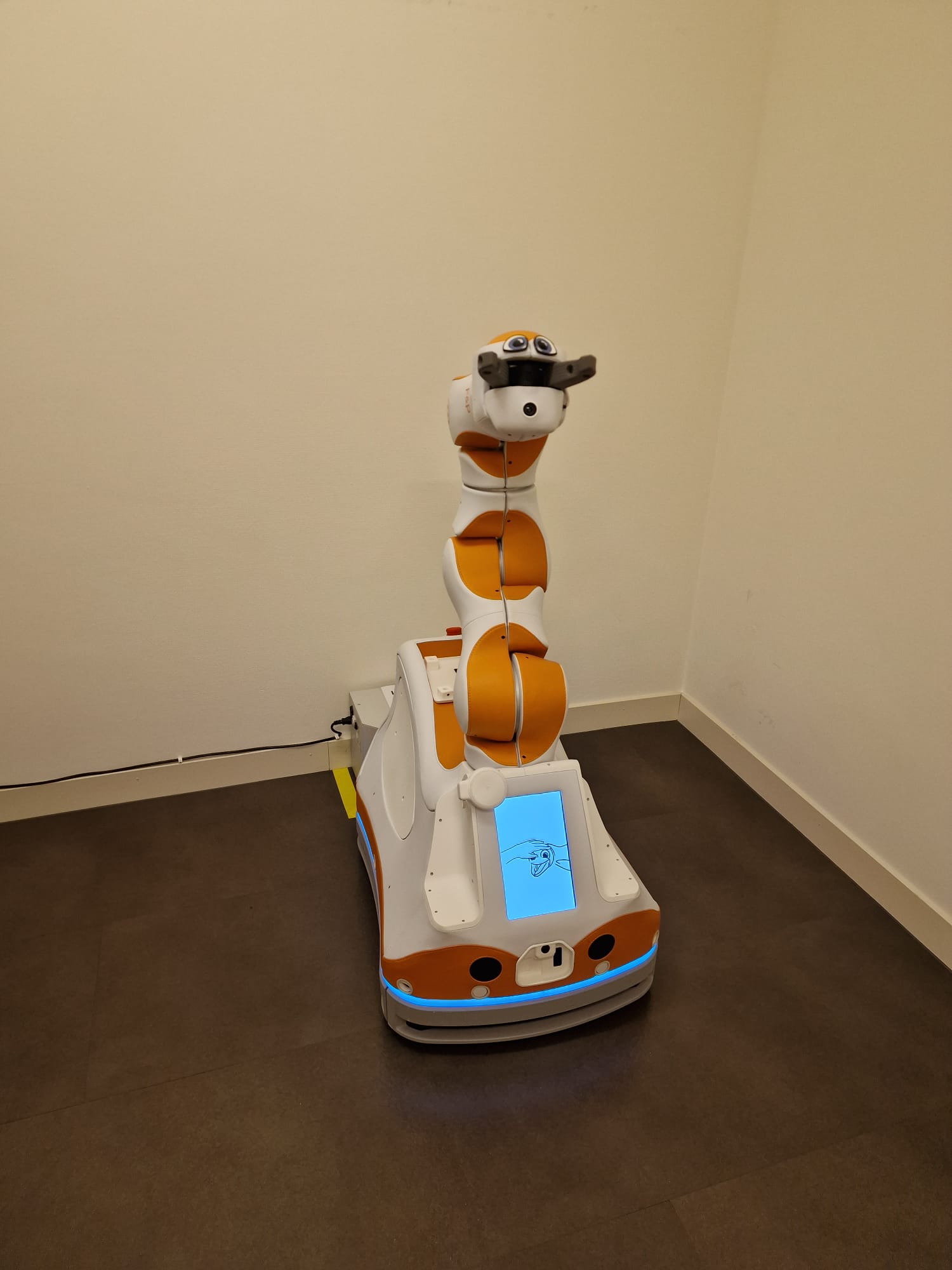
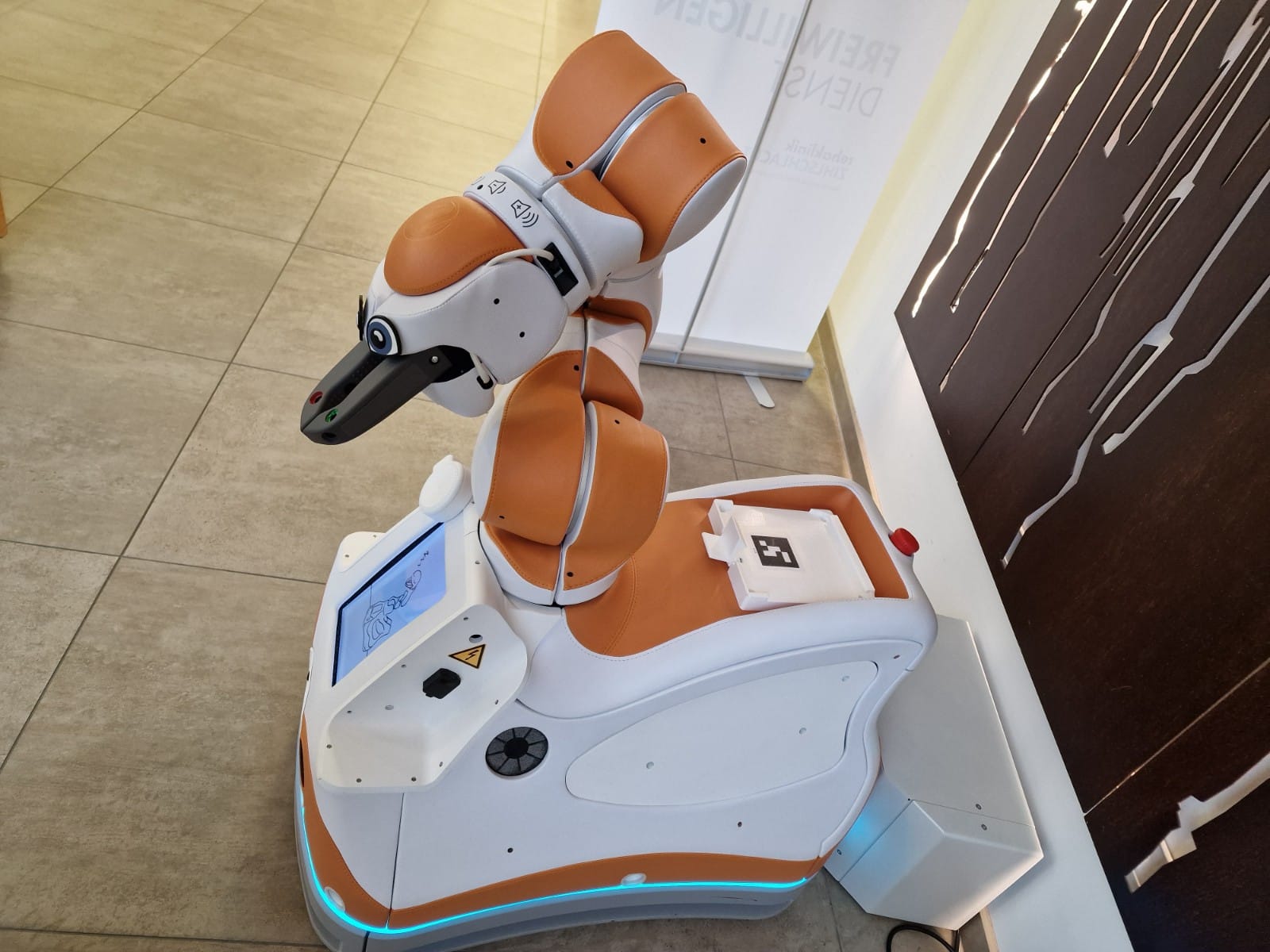
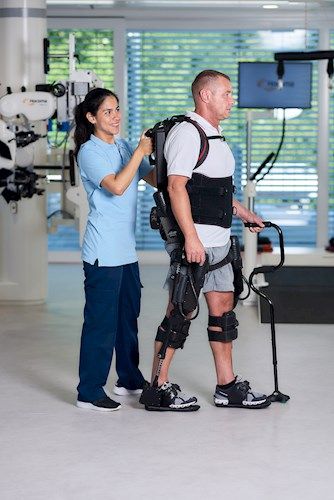
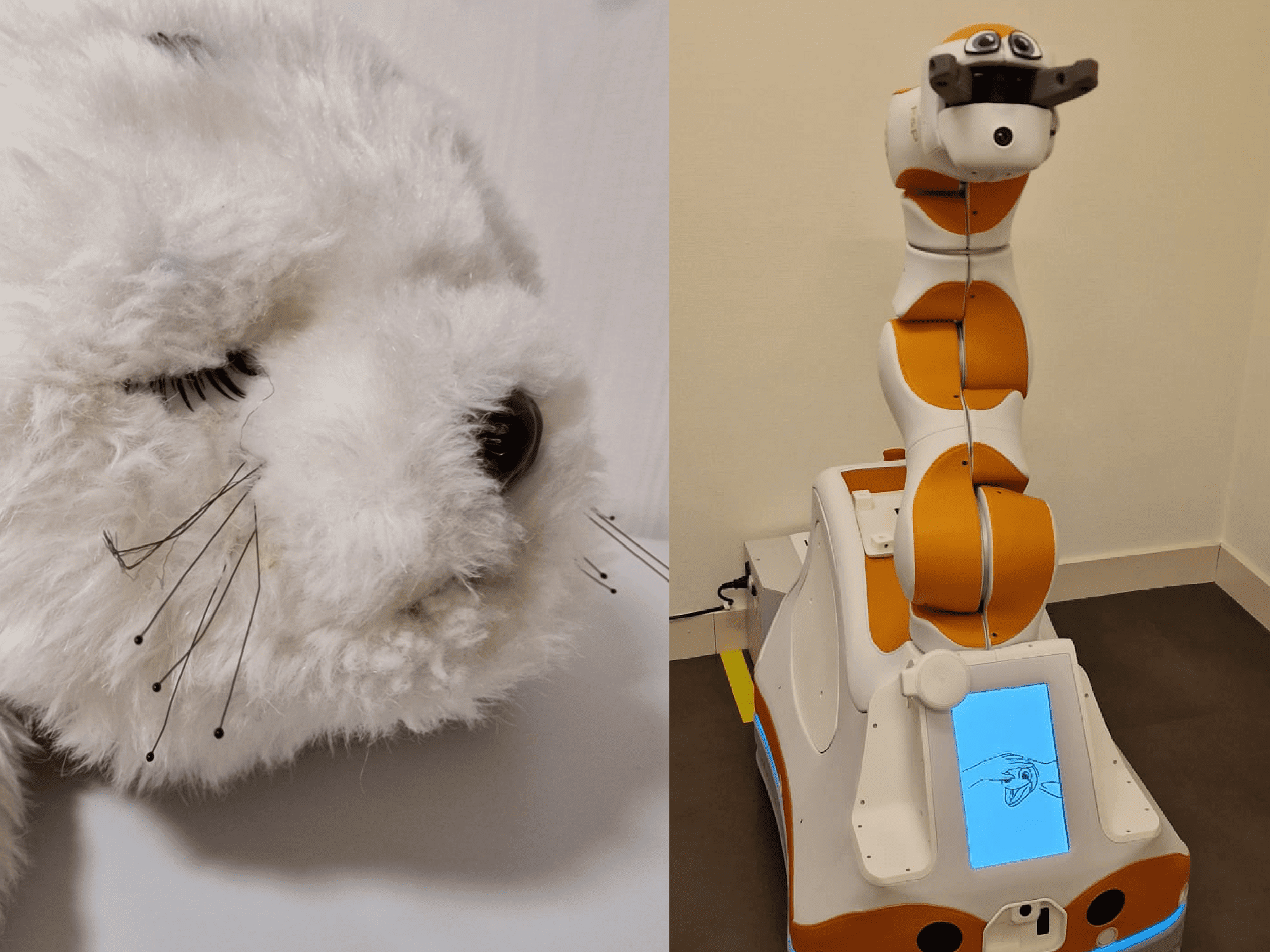
This paper focuses on three distinct robots: Lio, Paro, and an exoskeleton. These robots offer various values, such as enhancing care quality, economic benefits, emotional support, and health improvements. By assisting care workers with routine tasks, these robots free up more time for essential tasks, particularly personal care of patients, thus elevating the overall quality of care. Moreover, deploying robots could help ease the nursing shortage by taking over time-consuming tasks. Emotional value arises from robots designed for emotional support like Paro or those that bring joy to patients like Lio. Additionally, the exoskeleton reduces strain on the back, promoting long-term health, while Lio's disinfection capabilities contribute to infection prevention. These values are further expanded, discussed, and explored in the research.
Implications for practitioners
The following bullet points summarize the implications for practitioners important to keep in mind:
- The desire of care workers for relief is there. However, robotics still needs to be developed further to provide substantial relief. The functionality of the robots must therefore be further developed and expanded in order to meet the wishes of the care workers.
- Robots can generate great value in care for care workers, patients, and family members, but most robots are still in their infancy and have yet to be fully developed to be a substantial relief.
- To successfully integrate a robot, the whole environment must be prepared to onboard. It takes a lot of energy to master the integration successfully, and it is important to convince people repeatedly that a robot can add value once fully integrated.
- Robots in care lead, in any case, to an emotional reaction from the involved. Be this happy, with rejection, curious, fearful, or surprised. In order to integrate robots successfully, it is important to pick up and address different emotions.
Methods
The methodology section of the research paper outlines the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques employed to examine the value generated by robots in care work and the necessary prerequisites. The research design encompasses interviews and observations as the chosen approaches. Thirteen interviews and three observations were conducted, with a primary emphasis on the interviews. The research adopts an inductive approach, utilizing MaxQDA software to identify patterns and derive general conclusions. Purposive sampling was employed to select interview participants capable of providing valuable insights. Primary data was collected, with interviews being conducted in person, recorded, transcribed, and analyzed using MAXQDA. Observations occurred in care facilities utilizing robots, focusing on various integration aspects.